Role of data and machine learning in procurement
Data in procurement plays an important role as it allows an organisation to put data at the centre of its operations and then utilises insights derived from data to drive strategies and decision making.
Today, in any industry, one can certainly come across a story about how data is changing the face of the world. In 2015, data and analytics guru Bernard Marr said, “I firmly believe that big data and its implications will affect every single business—from Fortune 500 enterprises to mom-and-pop companies—and change how we do business, inside and out.” And boy, was he right!
The need for data-driven procurement
While most organisations don’t invest much resources in procurement it nevertheless ends up becoming one of the most crucial roles to drive success or failure. Data in procurement plays an important role as it allows an organisation to put data at the centre of its operations and then utilises insights derived from data to drive strategies and decision making.
Procurement is quickly evolving in response to rapid advances in technology, skills, and talent, changing consumer demands, and business practices. Businesses across a range of industries are using data more and more as the basis of their strategic planning and to measure business performance.
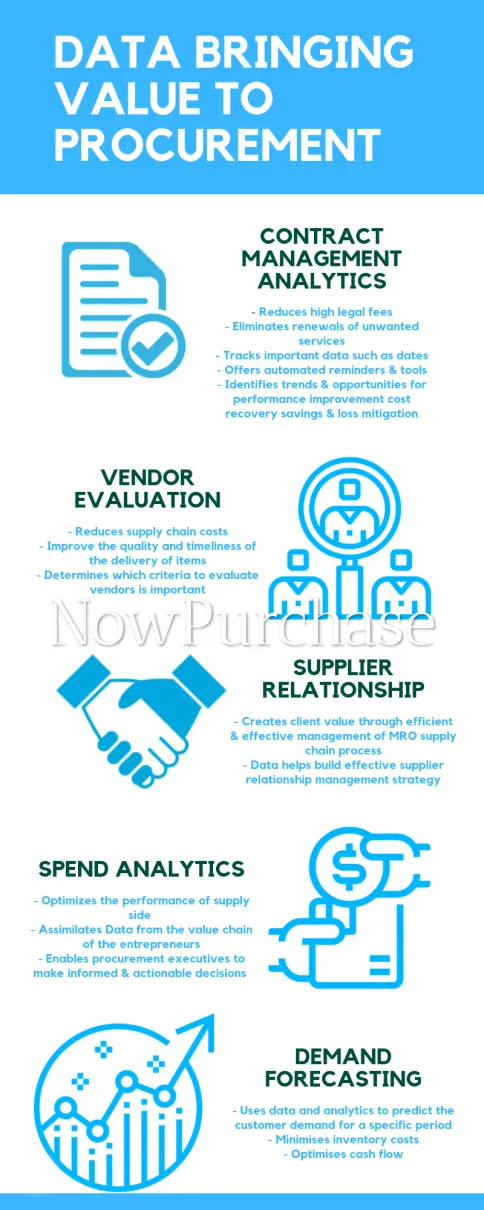
The main areas where data can bring value to the procurement performance are:
Contract management analytics: Data in this area helps improves business performance through visibility of risks, obligations, and opportunities in their contracts. Data can help immensely in identifying trends and opportunities for performance improvement, cost recovery, savings, and loss mitigation, thus leading to building stronger relationships with customers, suppliers, strategic partners, and other stake holders.
Vendor evaluation: Procurement managers are constantly faced with regular decision-making prior to approaching vendors for material specifications, costs, transports, as well as be prepared in case of change in requirement. Hence, there is a need to maintain a regularly updated database management system for procurement research and actual transactions. Vendor evaluation reduces supply chain costs, improves the quality and timeliness of the delivery of items, and also determines which vendor criteria is important to evaluate.
Supplier relationship: Companies are increasingly dependent on their supply chains to improve product quality, keep costs in check, and mitigate risks. As a result, maintaining supplier relationships are becoming an area of amplified management focus. Companies generate large amounts of data all along the supply chain that executives are learning to leverage. It is this collected data that can support more strategic supplier partnerships.
Spend analytics: Spend analytics is one of the key tools that organisations proactively use to identify saving opportunities, manage risks, and optimise buying power. Data from spend analysis can improve visibility into corporate spend, drive performance improvement, and cost savings, and enables procurement executives to make informed and actionable decisions.
Demand forecasting: Demand forecasting looks at data about your suppliers, whether they provide completed products or parts that are assembled further down the supply chain. This helps determine the amount that can be ordered or delivered in a specific timeframe. Data here allows organisations to keep a suitable volume in stock to meet customer demand, and at the same time reduce time, money, and effort.
Machine learning in procurement
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) have made their way into the business world based on the idea that systems can learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. ML is a data analysis method that automates analytical model building, and is a part of AI. Procurement is one department that could benefit from advancements in machine learning, namely due to the many repetitive and manual tasks that most buyers have to go through on a daily basis.
Three ways how ML can work at procurement level:
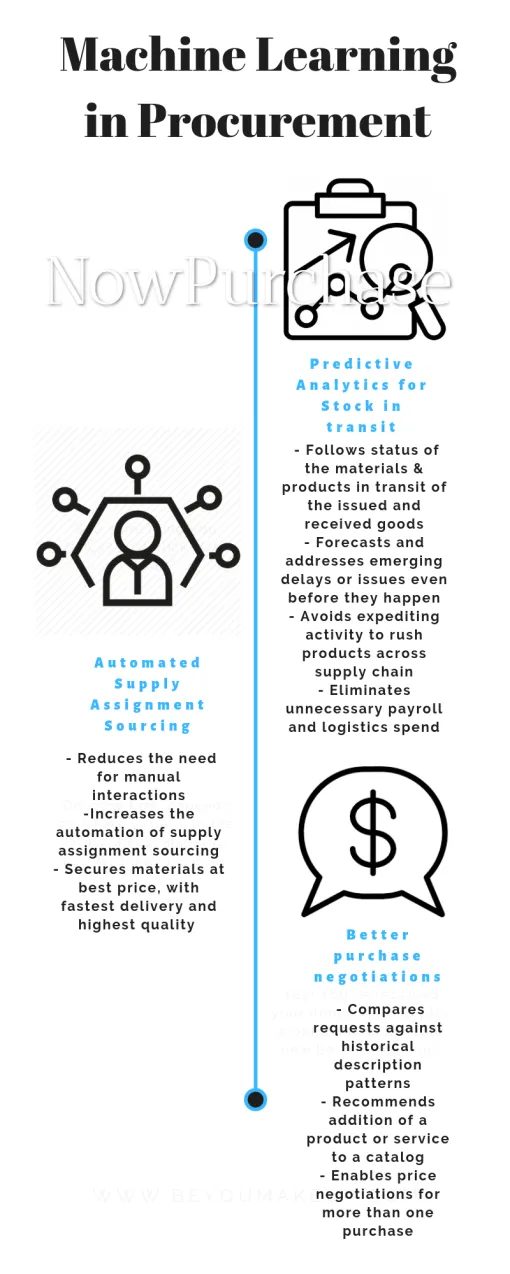
Apart from the stated points in the infograph, AI also helps in:
Spend classification: It is not a secret anymore that machines are found better at handling dull and repetitive tasks, and can achieve higher classification accuracy more efficiently than humans. No matter how much time we, as humans, spend cleaning up and classifying long-tail spend, the complexity of millions of line items of spend goes beyond time and resources.
Chatbot support: Chatbot in procurement can interact with users across platforms and provide contextual suggestions based on real transactions and purchase order data. Users, are now more comfortable asking chatbots for help, without thinking that the advice they are receiving is developed by AI.
Data and ML can bring a new frontier in procurement with the promise of transformative changes. Enterprises can leverage these to get actionable insights for improved business results. However, these possibilities mostly rely on data collection and analysis. Being able to collect data points, analyse them, and then turn them into tangible actions creates huge opportunities for the suppliers and the buyers.
(Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of YourStory.)
(Edited by Evelyn Ratnakumar)








